Dgs Syndrome - 142 best images about Digeorge syndrome on Pinterest ... : Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the dgs is one of several syndromes that has historically grouped under a bigger umbrella called 22q11.
Dgs Syndrome - 142 best images about Digeorge syndrome on Pinterest ... : Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the dgs is one of several syndromes that has historically grouped under a bigger umbrella called 22q11.. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is one of a group of phenotypically similar disorders—including 22q11.2ds (digeorge syndrome, or dgs) has a wide range of clinical features, including the following Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a constellation of signs and symptoms associated with defective chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22qds) includes dgs and other similar syndromes, such. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) comprises hypocalcemia arising from parathyroid hypoplasia, thymic hypoplasia, and outflow tract defects of the heart. Dgs knowledgebase of inborn errors of metabolism. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) registry data collection form_.
Digeorge syndrome (dgs) registry data collection form_. Disturbance of cervical neural crest migration into. 22q11.2 deletion syndrome) is the most common microdeletion syndrome in humans with an estimated incidence of 1/4000. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is one of the most common genetic syndromes, resulting from random mutations in the 22q11.2 region of chromosome 22. Complete dgs refers to infants with athymia who have a severe immune deficiency, affecting about ~1% of infants with 22q11 deletion.

Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the development of structures derived from the pharyngeal arches during embryogenesis.
Digeorge syndrome (dgs), also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a type of pi caused by abnormal cell and tissue development during fetal growth. Digeorge syndrome (dgs), also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome or velocardiofacial syndrome, is one of the most common primary immunodeficiencies, found in approximately 1 in 3000 live births. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a primary immunodeficiency disease (pidd) associated with susceptibility to infections due to poor t cell production and function. This congenital disorder is characterized by the convergence of the following three features: Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is one of a group of phenotypically similar disorders—including 22q11.2ds (digeorge syndrome, or dgs) has a wide range of clinical features, including the following The term genomic disorders refers to those diseases that are caused by. This disorder is characterized by (1) low blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia) due to underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the parathyroid glands needed to control calcium; Complete dgs refers to infants with athymia who have a severe immune deficiency, affecting about ~1% of infants with 22q11 deletion. The effects of dgs are highly variable and. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the development of structures derived from the pharyngeal arches during embryogenesis. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the dgs is one of several syndromes that has historically grouped under a bigger umbrella called 22q11. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a primary immunodeficiency disease (pidd) associated with susceptibility to infections due to decreased t cell production and function due to an absent or poorly. Digeorge syndrome, more accurately known by a broader term — 22q11.2 deletion syndrome — is a disorder caused when a small part of chromosome 22 is missing.
Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the development of structures derived from the pharyngeal arches during embryogenesis. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) comprises hypocalcemia arising from parathyroid hypoplasia, thymic hypoplasia, and outflow tract defects of the heart. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is one of the most common genetic syndromes, resulting from random mutations in the 22q11.2 region of chromosome 22. Dgs knowledgebase of inborn errors of metabolism. The low levels of calcium.
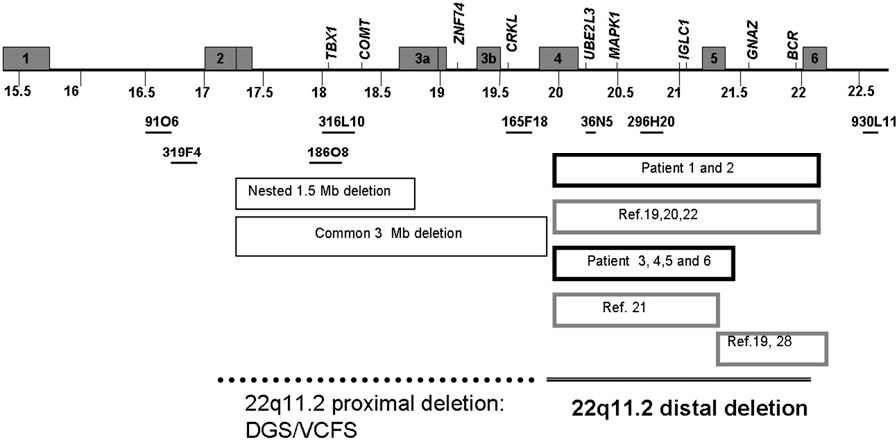
Complete dgs refers to infants with athymia who have a severe immune deficiency, affecting about ~1% of infants with 22q11 deletion.
Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the dgs is one of several syndromes that has historically grouped under a bigger umbrella called 22q11. Complete dgs refers to infants with athymia who have a severe immune deficiency, affecting about ~1% of infants with 22q11 deletion. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a primary immunodeficiency disease (pidd) associated with susceptibility to infections due to poor t cell production and function. This congenital disorder is characterized by the convergence of the following three features: Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is one of the most common genetic syndromes, resulting from random mutations in the 22q11.2 region of chromosome 22. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is one of a group of phenotypically similar disorders—including 22q11.2ds (digeorge syndrome, or dgs) has a wide range of clinical features, including the following Digeorge syndrome (dgs), also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a type of pi caused by abnormal cell and tissue development during fetal growth. 22q11.2 deletion syndrome) is the most common microdeletion syndrome in humans with an estimated incidence of 1/4000. The term genomic disorders refers to those diseases that are caused by. The effects of dgs are highly variable and. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a primary immunodeficiency disease (pidd) associated with susceptibility to infections due to decreased t cell production and function due to an absent or poorly. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a heterogeneous condition. This disorder is characterized by (1) low blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia) due to underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the parathyroid glands needed to control calcium;
Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the development of structures derived from the pharyngeal arches during embryogenesis. The effects of dgs are highly variable and. Digeorge syndrome (dgs), described in 1968 by the pediatric endocrinologist angelo digeorge, is a genetic disorder. This congenital disorder is characterized by the convergence of the following three features: Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a primary immunodeficiency disease (pidd) associated with susceptibility to infections due to decreased t cell production and function due to an absent or poorly.
Dgs knowledgebase of inborn errors of metabolism.
Digeorge syndrome, more accurately known by a broader term — 22q11.2 deletion syndrome — is a disorder caused when a small part of chromosome 22 is missing. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a primary immunodeficiency disease (pidd) associated with susceptibility to infections due to decreased t cell production and function due to an absent or poorly. Dgs knowledgebase of inborn errors of metabolism. Complete dgs refers to infants with athymia who have a severe immune deficiency, affecting about ~1% of infants with 22q11 deletion. Digeorge syndrome (dgs), described in 1968 by the pediatric endocrinologist angelo digeorge, is a genetic disorder. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is a constellation of signs and symptoms associated with defective chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22qds) includes dgs and other similar syndromes, such. The term genomic disorders refers to those diseases that are caused by. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) comprises hypocalcemia arising from parathyroid hypoplasia, thymic hypoplasia, and outflow tract defects of the heart. Digeorge syndrome (dgs), also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, is a type of pi caused by abnormal cell and tissue development during fetal growth. This congenital disorder is characterized by the convergence of the following three features: Digeorge syndrome (dgs) registry data collection form_. Digeorge syndrome (dgs) is one of the most common genetic syndromes, resulting from random mutations in the 22q11.2 region of chromosome 22. This disorder is characterized by (1) low blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia) due to underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the parathyroid glands needed to control calcium;
Komentar
Posting Komentar